What is SSL, TLS?
Digital certificates serve as proof of ownership of a public key and are typically digital documents that are “signed” by reputable organisations. By extension, they serve to validate the legitimacy of a server or a client.
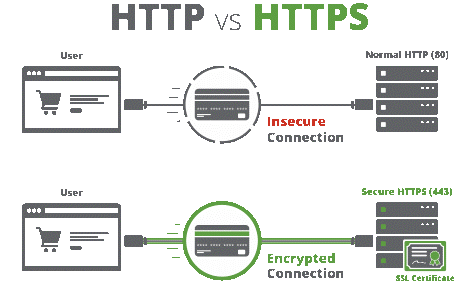
There are two popular cryptographic protocols – SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) for ensuring web communications with integrity, security, and resilience against unauthorised tampering.
Note: SSL was the predecessor of TLS, and the world began moving away from SSL once TLS was introduced in 1999. TLS is currently in its third iteration, and is called TLS 1.3, but SSL has been completely deprecated and no modern systems support SSL anymore).
Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts data sent over the Internet to ensure that eavesdroppers and hackers are unable to see what you transmit which is particularly useful for private and sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal correspondence.
Recent versions of all major web browsers currently support TLS, it is therefore recommended that all clients and servers insist on mandatory usage of TLS in their communications, and preferably the most recent version TLS 1.2 or 1.3.

How does TLS work?
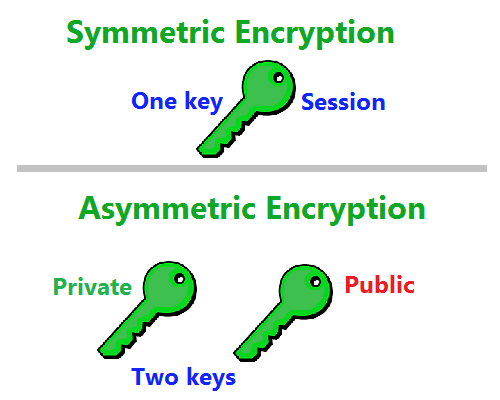
When sending data securely, TLS uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric cryptography because it offers a good balance between performance and security.
Asymmetric cryptography
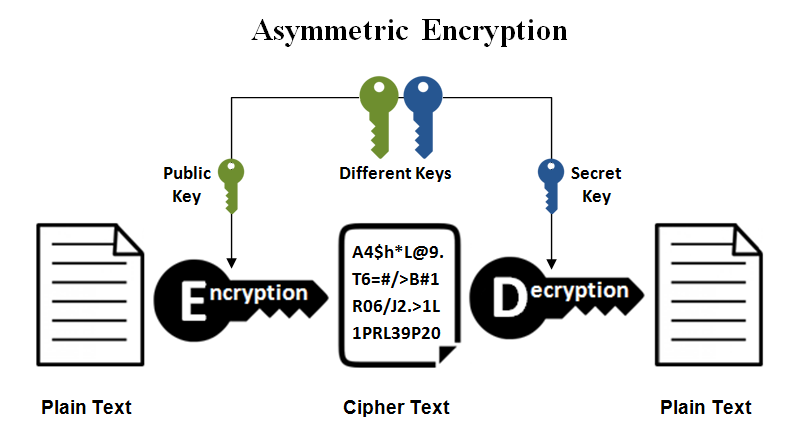
A public key and a private key are used in asymmetric cryptography. Although the private key and the public key are mathematically connected, it would be computationally difficult to deduce the private key from the public key given a long enough key length. This allows the public key of the recipient to be used by the sender to encrypt the data they wish to send to them, but that data can only be decrypted with the private key of the recipient.
Asymmetric cryptography has the benefit of allowing encryption keys to be shared without the need for security, but the mathematical link between public and private keys necessitates substantially higher key sizes. The recommended minimum key length is 1024 bits, with 2048 bits preferred; however, this makes asymmetric encryption too slow for many applications because it requires up to a thousand times more computation than symmetric keys of equivalent strength (for example, a 2048-bit asymmetric key is roughly equivalent to a 112-bit symmetric key).
Symmetric cryptography encrypts and decrypts data using a secret key that is shared between the sender and the recipient.
The SSL/TLS Handshake or Encryption Overview?
Asymmetric and symmetric encryption are both used by SSL/TLS to safeguard the confidentiality and integrity of data while it is in transit. A client and a server establish a secure session using asymmetric encryption, and during the secure session, data is exchanged using symmetric encryption.
To use SSL/TLS encryption, a website needs an SSL/TLS certificate for its web server and domain name. When the certificate is installed, the client and server can safely negotiate the degree of encryption by performing the following actions:
- Client initiates connection on the server using a secure URL (HTTPS not http).
- Server in response will sends its certificate and public key to the client.
- Client verifies these details with its Root Certification Authority and ensure if the certificate is legitimate.
- Post that both client and server negotiate to the strongest type of encryption which they can support.
- Now client starts encrypting the session (secret) key with the server’s public key, and sends it back to the server.
- Server will decrypt the client communication with its private key, and the secure session is established.
- Session key (symmetric encryption) is now used to encrypt and decrypt data transmitted between the client and server.

The BIG-IP Client SSL profile enables the BIG-IP system to accept and terminate client requests that are sent using a fully SSL-encapsulated protocol. It also provides a number of configurable settings for managing client-side SSL connections. Typically, you need to set only some of the available settings and keep the remaining settings at their default values unless otherwise advised by F5 Support.

We also offer a diverse library of pre-recorded videos for any online training or buy self-paced courses.
“Get enrolled now”.







Keep Learning! Keep Growing! Keep investing!
Welcome to NetMinion Solutions, a leading education training institute/company to nurture minds and fostering a passion for learning. No matter if you are a beginner or a professional – our dedicated faculty and state-of-the-art facilities create an enriching environment where you can explore, innovate, and grow exponentially – academically and personally both.
We are committed to practical learning and provide cutting-edge lab solutions, to enhance your learning journey – including CCNA, CCNP & CCIE, data center, Wireless, Cloud, VMware, F5 -LTM, GTM, ASM, APM, Palo Alto, SD-WAN, Checkpoint, ACI and list goes on.
